| Exam Name: | Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals | ||
| Exam Code: | SC-900 Dumps | ||
| Vendor: | Microsoft | Certification: | Microsoft Certified: Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals |
| Questions: | 210 Q&A's | Shared By: | arianna |
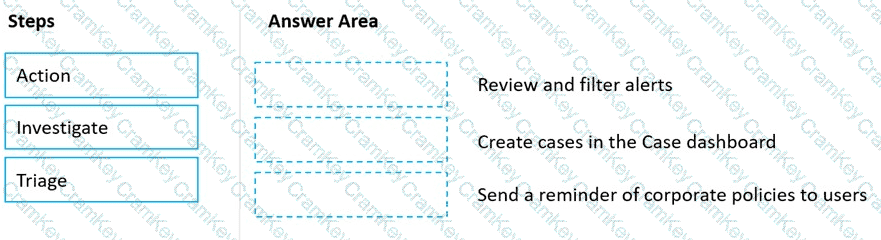
Match the Microsoft 365 insider risk management workflow step to the appropriate task.
To answer, drag the appropriate step from the column on the left to its task on the right. Each step may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point

Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Which Microsoft Defender for Cloud metric displays the overall security health of an Azure subscription?