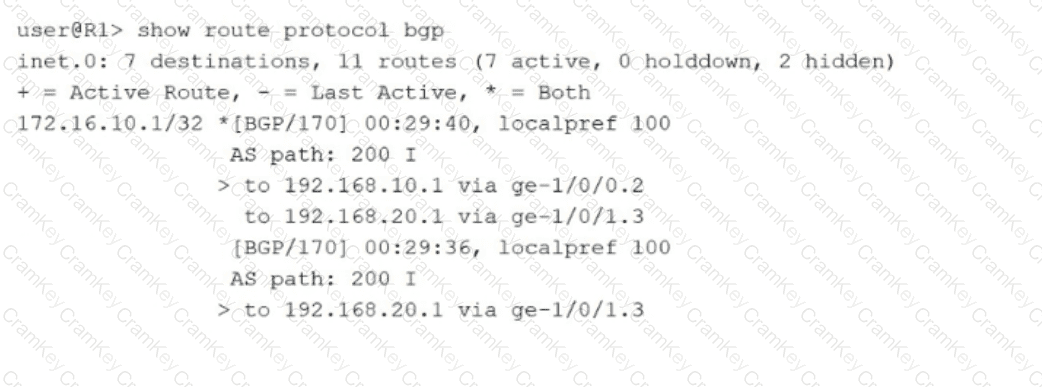
The exhibit shows the output of the command show route protocol bgp on router R1 for the prefix 172.16.10.1/32. To determine the correct characteristics of this route, we analyze the specific BGP attributes and next-hop information provided in the routing table entry:
Multipath Parameter (Option B): The routing table shows two distinct paths for the prefix 172.16.10.1/32. The first path has two next hops (192.168.10.1 and 192.168.20.1) and is marked with the plus symbol (+) and the asterisk (*), indicating it is both an active and the best route. The presence of multiple next hops being used simultaneously for a single BGP path is a clear indication that the multipath parameter is enabled in the BGP configuration. In Junos OS, BGP multipath allows the installation of multiple equal-cost BGP paths into the forwarding table to facilitate load balancing.
Available Next Hops (Option C): The output explicitly lists two functional next hops for the active path: 192.168.10.1 via ge-1/0/0.2 and 192.168.20.1 via ge-1/0/1.3. Both show an outgoing interface, confirming that this route has two next hops available for traffic forwarding.
IBGP vs. EBGP (Option A): The BGP routes shown have an AS path of 200 I. This indicates the routes were learned from an external Autonomous System (AS 200). Furthermore, the protocol preference is 170. In Junos OS, the default preference for External BGP (EBGP) is 170, whereas the default preference for Internal BGP (IBGP) is 200. Therefore, this configuration is for EBGP, not IBGP.
Hidden Next Hops (Option D): The summary line at the top of the exhibit mentions that there are "2 hidden" routes in the inet.0 table. However, these hidden routes are not the next hops for the 172.16.10.1/32 prefix. A hidden route is a prefix that was rejected by policy or has an unreachable next hop; it is not a "hidden next hop" belonging to an active route.