| Exam Name: | Management Accounting | ||
| Exam Code: | P1 Dumps | ||
| Vendor: | CIMA | Certification: | CIMA Operational |
| Questions: | 260 Q&A's | Shared By: | elsie-mae |
A company is preparing its annual budget and is estimating the number of units of Product A that it will sell in each quarter of year 2. Past experience has shown that the trend for sales of the product is represented by the following relationship:
y = a + bx where
y = number of sales units in the quarter a = 10,000 units b = 3,000 units x = the quarter number where 1 = quarter 1 of year 1
Actual sales of Product A in Year 1 were affected by seasonal variations and were as follows:
Quarter 1:14,000 units Quarter2: 18,000 units Quarter 3: 18,000 units Quarter 4: 20,000 units
Calculate the expected sales of Product A (in units) for each quarter of year 2, after adjusting for seasonal variations using the additive model.
A company has budgeted to produce 5,000 units of Product B per month. The opening and closing inventories of Product B for next month are budgeted to be 400 units and 900 units respectively. The budgeted selling price and variable production costs per unit for Product B are as follows:

Total budgeted fixed production overheads are $29,500 per month. The company absorbs fixed production overheads on the basis of the budgeted number of units produced. The budgeted profit for Product B for next month, using absorption costing, is $20,700.
Prepare a marginal costing statement which shows the budgeted profit for Product B for next month.
What was the difference between the profit calculation using marginal costing and the profit calculation using absorption costing?
JRL manufactures two products from different combinations of the same resources. Unit selling prices and unit cost details for each product are as follows:
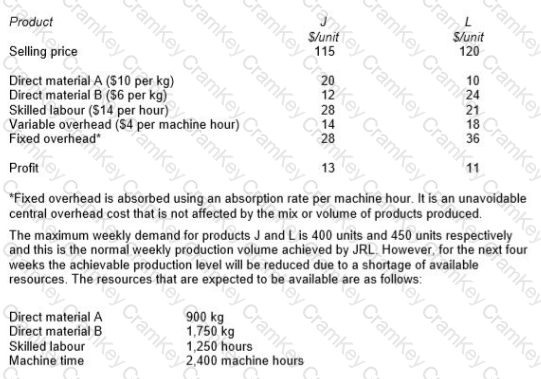
* Refer to your answer in the previous question.
The optimal solution to the previous question shows that the shadow prices of skilled labour and direct material A are as follows:
Skilled labour $ Nil Direct Material A $11.70
Explain the relevance of these values to the management of JRL.
Select ALL the true statements.
MDS is facing a temporary shortage of Material H which is used to produce all three of its products.
In order to maximise its profitability, which product should be manufactured first?