| Exam Name: | Microsoft Azure Administrator | ||
| Exam Code: | AZ-104 Dumps | ||
| Vendor: | Microsoft | Certification: | Azure Administrator Associate |
| Questions: | 428 Q&A's | Shared By: | aayan |
You create an Azure VM named VM1 that runs Windows Server 2019.
VM1 is configured as shown in the exhibit (Click the Exhibit tab.)
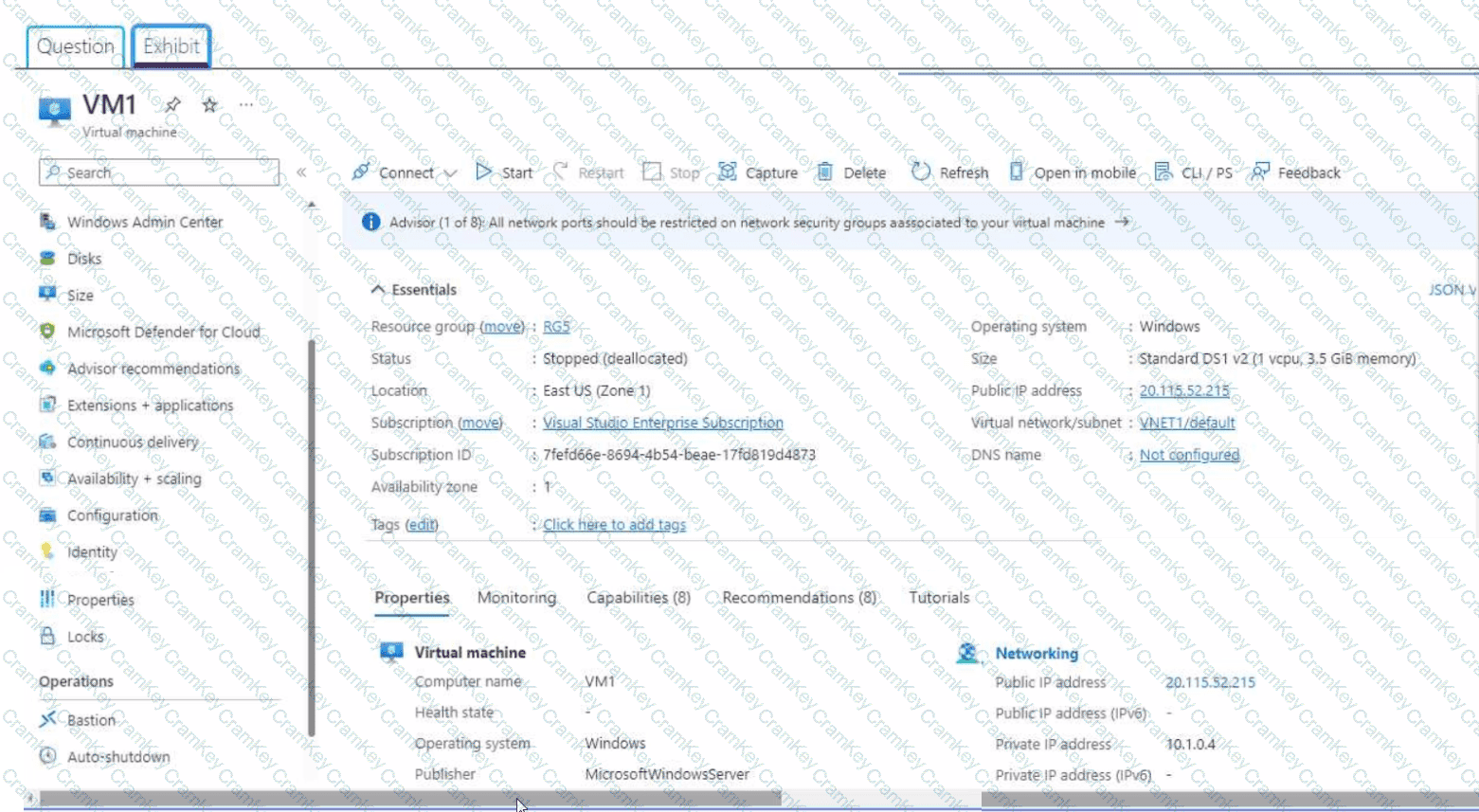
You need to enable Desired State Configuration for VM1.
What should you do first?
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to deploy a storage account named storage' by using the following Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
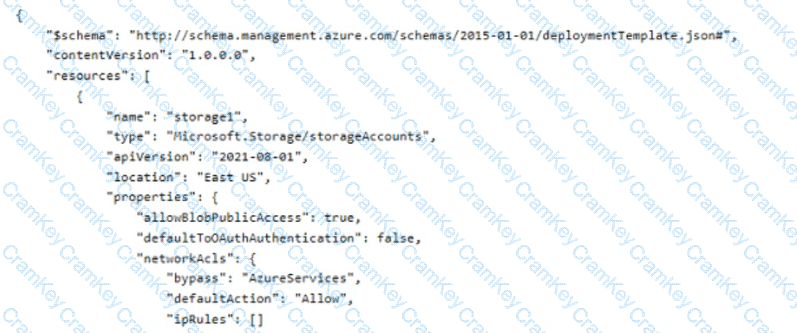
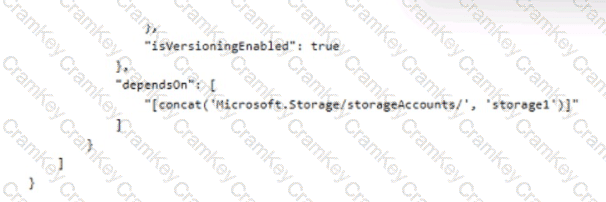
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

You have an Azure Storage account that contains 5,000 blobs accessed by multiple users.
You need to ensure that the users can view only specific blobs based on blob index tags.
What should you include in the solution?
You need to define a custom domain name for Azure AD to support the planned infrastructure.
Which domain name should you use?